Subversion version control system
If you're a user or system administrator pondering the use of Subversion, the first question you should ask yourself is: "Is this the right tool for the job?" Subversion is a fantastic hammer, but be careful not to view every problem as a nail.
If you need to archive old versions of files and directories, possibly resurrect them, or examine logs of how they've changed over time, then Subversion is exactly the right tool for you. If you need to collaborate with people on documents (usually over a network) and keep track of who made which changes, then Subversion is also appropriate. This is why Subversion is so often used in software development environments—working on a development team is an inherently social activity, and Subversion makes it easy to collaborate with other programmers. Of course, there's a cost to using Subversion as well: administrative overhead. You'll need to manage a data repository to store the information and all its history, and be diligent about backing it up. When working with the data on a daily basis, you won't be able to copy, move, rename, or delete files the way you usually do. Instead, you'll have to do all of those things through Subversion.
Assuming you're fine with the extra workflow, you should still make sure you're not using Subversion to solve a problem that other tools solve better. For example, because Subversion replicates data to all the collaborators involved, a common misuse is to treat it as a generic distribution system. People will sometimes use Subversion to distribute huge collections of photos, digital music, or software packages. The problem is that this sort of data usually isn't changing at all. The collection itself grows over time, but the individual files within the collection aren't being changed. In this case, using Subversion is “overkill.” There are simpler tools that efficiently replicate data without the overhead of tracking changes, such as rsync or unison.
In early 2000, CollabNet, Inc. began seeking developers to write a replacement for CVS. CollabNet offered a collaboration software suite called CollabNet Enterprise Edition (CEE), of which one component was version control. Although CEE used CVS as its initial version control system, CVS's limitations were obvious from the beginning, and CollabNet knew it would eventually have to find something better. Unfortunately, CVS had become the de facto standard in the open source world largely because there wasn't anything better, at least not under a free license. So CollabNet determined to write a new version control system from scratch, retaining the basic ideas of CVS, but without the bugs and misfeatures.
In February 2000, they contacted Karl Fogel, the author of Open Source Development with CVS (Coriolis, 1999), and asked if he'd like to work on this new project. Coincidentally, at the time Karl was already discussing a design for a new version control system with his friend Jim Blandy. In 1995, the two had started Cyclic Software, a company providing CVS support contracts, and although they later sold the business, they still used CVS every day at their jobs. Their frustration with CVS had led Jim to think carefully about better ways to manage versioned data, and he'd already come up with not only the Subversion name, but also the basic design of the Subversion data store. When CollabNet called, Karl immediately agreed to work on the project, and Jim got his employer, Red Hat Software, to essentially donate him to the project for an indefinite period of time. CollabNet hired Karl and Ben Collins-Sussman, and detailed design work began in May 2000. With the help of some well-placed prods from Brian Behlendorf and Jason Robbins of CollabNet, and from Greg Stein (at the time an independent developer active in the WebDAV/DeltaV specification process), Subversion quickly attracted a community of active developers. It turned out that many people had encountered the same frustrating experiences with CVS and welcomed the chance to finally do something about it.
The original design team settled on some simple goals. They didn't want to break new ground in version control methodology, they just wanted to fix CVS. They decided that Subversion would match CVS's features and preserve the same development model, but not duplicate CVS's most obvious flaws. And although it did not need to be a drop-in replacement for CVS, it should be similar enough that any CVS user could make the switch with little effort.
After 14 months of coding, Subversion became “self-hosting” on August 31, 2001. That is, Subversion developers stopped using CVS to manage Subversion's own source code and started using Subversion instead.
While CollabNet started the project, and still funds a large chunk of the work (it pays the salaries of a few full-time Subversion developers), Subversion is run like most open source projects, governed by a loose, transparent set of rules that encourage meritocracy. In 2009, CollabNet worked with the Subversion developers towards the goal of integrating the Subversion project into the Apache Software Foundation (ASF), one of the most well-known collectives of open source projects in the world. Subversion's technical roots, community priorities, and development practices were a perfect fit for the ASF, many of whose members were already active Subversion contributors. In early 2010, Subversion was fully adopted into the ASF's family of top-level projects, moved its project web presence to , and was rechristened “Apache Subversion”.
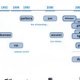
Subversion's Architecture
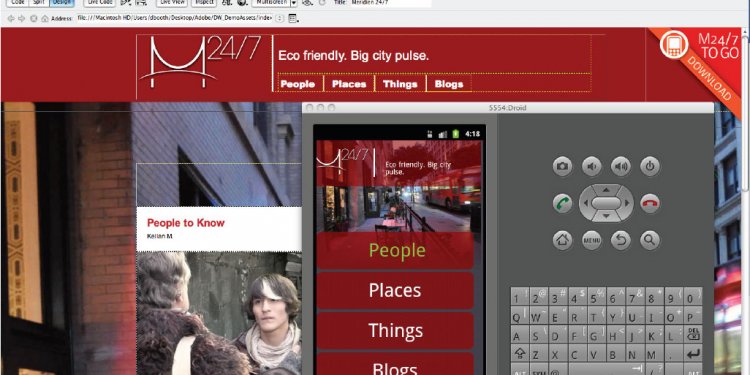
Figure 1, “Subversion's architecture” illustrates a “mile-high” view of Subversion's design.
Figure 1. Subversion's architecture
On one end is a Subversion repository that holds all of your versioned data. On the other end is your Subversion client program, which manages local reflections of portions of that versioned data. Between these extremes are multiple routes through a Repository Access (RA) layer, some of which go across computer networks and through network servers which then access the repository, others of which bypass the network altogether and access the repository directly.
Subversion, once installed, has a number of different pieces. The following is a quick overview of what you get. Don't be alarmed if the brief descriptions leave you scratching your head—plenty more pages in this book are devoted to alleviating that confusion.
svnThe command-line client program
svnversion