March 14, 2020
Types of Electrical control Systems
Before I introduce you the theory of control system it is very essential to know the various types of control systems. Now there are various types of systems, we are going to discuss only those types of systems that will help us to understand the theory of control system and detail description of these types of system are given below:
Linear Control Systems
In order to understand the linear control system, we should know the principle of superposition. The principle of superposition theorem includes two the important properties and they are explained below: Homogeneity : A system is said to be homogeneous, if we multiply input with some constant ‘A’ then output will also be multiplied by the same value of constant (i.e. A). Additivity: Suppose we have a system ‘S’ and we are giving the input to this system as ‘a1’ for the first time and we are getting output as ‘b1’ corresponding to input ‘a1’. On second time we are giving input ‘a2’ and correspond to this we are getting output as ‘b2’. Now suppose this time we giving input as summation of the previous inputs ( i.e. a1 + a2 ) and corresponding to this input suppose we are getting output as (b1 + b2) then we can say that system ‘S’ is following the property of additivity. Now we are able to define the linear control systems as those types of control systems which follow the principle of homogeneity and additivity.Examples of Linear Control System
Consider a purely resistive network with a constant DC source. This circuit follows the principle of homogeneity and additivity. All the undesired effects are neglected and assuming ideal behavior of each element in the network, we say that we will get linear voltage and current characteristic. This is the example of linear control system.Non-linear Systems
We can simply define non linear control system as all those system which do not follow the principle of homogeneity. In practical life all the systems are non-linear system.Examples of Non-linear System
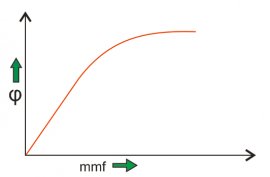
A well known example of non-linear system is magnetization curve or no load curve of a DC machine. We will discuss briefly no load curve of DC machines here: No load curve gives us the relationship between the air gap flux and the field winding mmf. It is very clear from the curve given below that in the beginning there is a linear relationship between winding mmf and the air gap flux but after this, saturation has come which shows the non linear behavior of the curve or characteristics of the non linear control system.
Analog or Continuous System
In these types of control system we have continuous signal as the input to the system. These signals are the continuous function of time. We may have various sources of continuous input signal like sinusoidal type signal input source, square type of signal input source, signal may be in the form of continuous triangle etc.Digital or Discrete System
In these types of control system we have discrete signal (or signal may be in the form of pulse) as the input to the system. These signals have the discrete interval of time. We can convert various sources of continuous input signal like sinusoidal type signal input source, square type of signal input source etc into discrete form using the switch.Now there are various advantages of discrete or digital system over the analog system and these advantages are written below:
- Digital systems can handle non linear control systems more effectively than the analog type of systems.
- Power requirement in case of discrete or digital system is less as compared to analog systems.
- Digital system has higher rate of accuracy and can perform various complex computations easily as compared to analog systems.
- Reliability of digital system is more as compared to analog system. They also have small and compact size.
- Digital system works on the logical operations which increases their accuracy many times.
- Losses in case of discrete systems are less as compared to analog systems in general.