Applications of Control Systems in Industry
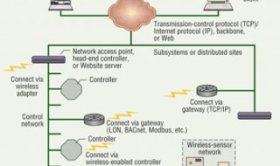
 The demand for installed wireless control networks in industrial buildings continues to grow because of the attributes inherent to wireless communication, such as flexibility, straightforward installation, and low material/labor costs. However, some industry leaders still hesitate to invest in wireless solutions because of concerns about the reliability and security of existing wireless standards and compatibility with established control-network infrastructures.
The demand for installed wireless control networks in industrial buildings continues to grow because of the attributes inherent to wireless communication, such as flexibility, straightforward installation, and low material/labor costs. However, some industry leaders still hesitate to invest in wireless solutions because of concerns about the reliability and security of existing wireless standards and compatibility with established control-network infrastructures.
This article discusses eligibility and deployment aspects of wireless controls and how wireless controls can be applied in HVAC systems in a complex industrial-building environment to achieve greater energy-policy compliance.
Historically, process industries have adopted new technologies cautiously. However, because energy costs are increasing rapidly, facility executives feel an escalating need to reduce energy consumption by means of more sophisticated building controls and HVAC-optimization strategies. According to a study conducted by ARC Advisory Group, a research and advisory firm for manufacturing, energy, and supply-chain solutions, the worldwide market for wireless technology in industrial automation will have an annual growth rate of 32 percent, reaching $1.1 billion in 2012.
CONCERNS ABOUT WIRELESS NETWORKS IN INDUSTRIAL ENVIRONMENTS
Skepticism about wireless control systems still looms. Scalability and flexibility rarely are in question. However, security, interoperability, and reliability issues cause some engineers to question whether to abandon their wired designs for wireless. Additionally, battery-powered wireless devices are unacceptable to system integrators endeared to the concept of “install-and-forget” solutions.
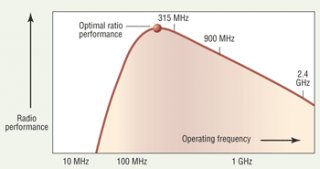
Meanwhile, wireless technologies and communication protocols have matured, with improved security, interference immunity, and reliability. When retrofitting older buildings with modern controls, wireless solutions can simplify energy-saving installations. Combined with intelligent building-automation systems (BAS), wireless technology can offer potential operational savings and reliable performance.