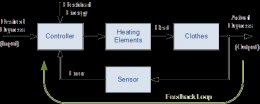
Feedback control system Block diagram
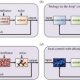
 The block diagram is to represent a control system in diagram form. In other words practical representation of a control system is its block diagram. It is not always convenient to derive the entire transfer function of a complex control system in a single function. It is easier and better to derive transfer function of control element connected to the system, separately. The transfer function of each element is then represented by a block and they are then connected together with the path of signal flow. For simplifying a complex control system, block diagrams are used. Each element of the control system is represented with a block and the block is the symbolic representation of transfer function of that element. A complete control system can be represented with a required number of interconnected such blocks. In the figure below, there are two elements with transfer function Gone(s) and Gtwo(s). Where Gone(s) is the transfer function of first element and Gtwo(s) is the transfer function of second element of the system.
The block diagram is to represent a control system in diagram form. In other words practical representation of a control system is its block diagram. It is not always convenient to derive the entire transfer function of a complex control system in a single function. It is easier and better to derive transfer function of control element connected to the system, separately. The transfer function of each element is then represented by a block and they are then connected together with the path of signal flow. For simplifying a complex control system, block diagrams are used. Each element of the control system is represented with a block and the block is the symbolic representation of transfer function of that element. A complete control system can be represented with a required number of interconnected such blocks. In the figure below, there are two elements with transfer function Gone(s) and Gtwo(s). Where Gone(s) is the transfer function of first element and Gtwo(s) is the transfer function of second element of the system.
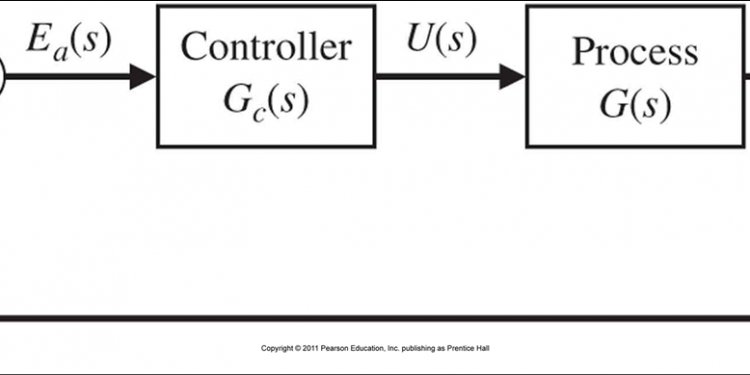
In addition to that, the diagram also shows there is a feedback path through which output signal C(s) is fed back and compared with the input R(s) and the difference between input and output E(s) = R(s) – C(s) is acting as actuating signal or error signal. In each block of diagram, the output and input are related together by transfer function. Where, transfer function where, C(s) is the output and R(s) is the input of that particular block. A complex control system consists of several blocks. Each of them has its own transfer function. But overall transfer function of the system is the ratio of transfer function of final output to transfer function of initial input of the system. This overall transfer function of the system can be obtained by simplifying the control system by combining this individual blocks, one by one. Technique of combining of these blocks is referred as block diagram reduction technique. For successful implementation of this technique, some rules for block diagram reduction to be followed. Let us discuss these rules, one by one for reduction of block diagram of control system.
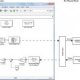
If the transfer function of input of control system is R(s) and corresponding output is C(s), and the overall transfer function of the control system is G(s), then the control system can be represented as