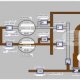
Distributed control system block diagram
 Advancements in Intelligent Instrumentation and Remote Terminal Units (RTUs) / Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) have made the process-control solutions in many of the industries to be easily managed and operated by utilizing the benefits of a SCADA system. SCADA is popular in several applications like process industries, oil and gas, electric power generation, distribution and utilities, water and waste control, agriculture/irrigation, manufacturing, transportation systems, and so on. Let us know about the SCADA system‘s working principle in brief from this article.
Advancements in Intelligent Instrumentation and Remote Terminal Units (RTUs) / Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) have made the process-control solutions in many of the industries to be easily managed and operated by utilizing the benefits of a SCADA system. SCADA is popular in several applications like process industries, oil and gas, electric power generation, distribution and utilities, water and waste control, agriculture/irrigation, manufacturing, transportation systems, and so on. Let us know about the SCADA system‘s working principle in brief from this article.
What is SCADA System?
 SCADA stands for Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition; it is an industrial computer-based control system employed to gather and analyze the real-time data to keep track, monitor and control industrial equipments in different types of industries. Consider the application of SCADA in power systems for operation and control.
SCADA stands for Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition; it is an industrial computer-based control system employed to gather and analyze the real-time data to keep track, monitor and control industrial equipments in different types of industries. Consider the application of SCADA in power systems for operation and control.
SCADA in power system can be defined as the power distribution application which is typically based on the software package. The electrical distribution system consists of several substations; these substations will have multiple numbers of controllers, sensors and operator-interface points.
In general, for controlling and monitoring a substation in real time (PLCs) Programmable Logic Controllers, Circuit breakers and Power monitors are used. Data is transmitted from the PLCs and other devices to a computer-based-SCADA node located at each substation. One or more computers are located at different centralized control and monitoring points.
One or more computers are located at different centralized control and monitoring points.
SCADA system usage have became popular from the 1960s with the increase in need of monitoring and controlling the equipment. Early systems built using mainframe computers were expensive as they were manually operated and monitored. But the recent advancements in technology have made-advanced, automated SCADA systems with maximum efficiency at reduced cost, according to the alarming requirements of the company.
 SCADA Basics
SCADA Basics
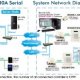
Before discussing about the architecture of SCADA and different types of SCADA systems, primarily we must know a few SCADA basics. Consider the block diagram of SCADA system shown in the figure which consists of different blocks, namely Human-machine Interface (HMI), Supervisory system, Remote terminal units, PLCs, Communication infrastructure and SCADA Programming.
1. Human-machine Interface (HMI)
It is an input-output device that presents the process data to be controlled by a human operator. It is used by linking to the SCADA system’s software programs and databases for providing the management information, including the scheduled maintenance procedures, detailed schematics, logistic information, trending and diagnostic data for a specific sensor or machine. HMI systems facilitate the operating personnel to see the information graphically.