October 2, 2017
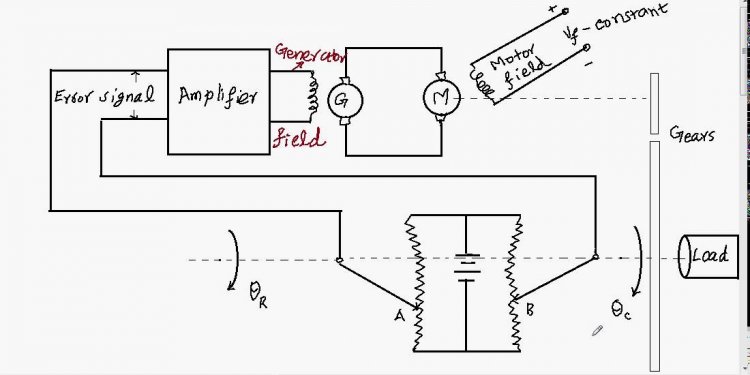
Closed loop position control system

Electric Drives - Motor Controllers and Control Systems
(Description and Applications)
Purpose
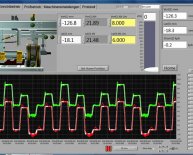
For many years the motor controller was a box which provided the motor speed control and enabled the motor to adapt to variations in the load. Designs were often lossy or they provided only crude increments in the parameters controlled.
Modern controllers may incorporate both power electronics and microprocessors enabling the control box to take on many more tasks and to carry them out with greater precision. These tasks include:
- Controlling the dynamics of the machine and its response to applied loads.
(speed, torque and efficiency of the machine or the position of its moving elements.) - Providing electronic commutation.
- Enabling self starting of the motor.
- Protecting the motor and the controller itself from damage or abuse.
- Matching the power from an available source to suit the motor requirements (voltage, frequency, number of phases). This is an example of "Power Conditioning" whose purpose is to provide pure DC or sinewave power free from harmonics or interference. Although it could be an integral part of a generator control system, more generally, power conditioning could also be provided by a separate free standing module operating on any power source.