Define open loop system
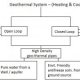
Open-loop systems are set up to achieve desired results, but there's no way of checking if the results have been achieved. For example, an old-fashioned heating system might include:
- input: an on-off switch
- process: boiler (water heater) and pump
- output: radiator
The aim of the system would be to heat a house. When turned on, the heating would stay on until it was turned off, regardless of whether the house remained cold or became too hot.
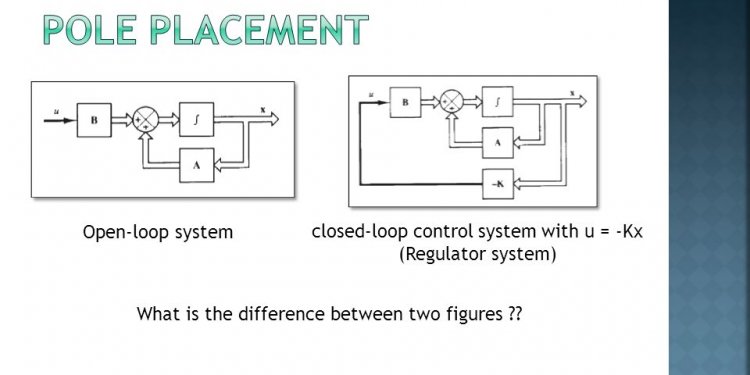
Closed-loop systems
Closed-loop systems are able to correct in order to meet target results. Normally a sensor is used to look at the output and adjust the process accordingly. This is called feedback.
For example, considering the heating system above, a thermostat could be added to measure the temperature of a room and compare it to a set target. If the room became too cold, the thermostat would turn the heating on and if the temperature became too hot the system would be turned off. The effectiveness of the system could be analysed by monitoring how good it is at keeping the room at the target temperature.