Perpetual inventory control system
Businesses keep track of inventory through inventory systems. This lesson will focus on one type of system - perpetual inventory system. It will define perpetual inventory system, examine its advantages and give an example.
Perpetual Inventory System Defined
A perpetual inventory system, or continuous inventory system, is an inventory control system that allows businesses to keep a real-time account of inventory on hand. The widespread use of computers after the 1970s increased this systems popularity because businesses were able to more easily keep track of inventory as it sold. Barcodes, radiofrequency identification scanners (known as RFID), and point of sale systems (also known as POS) provided support for this system by quickly inputting inventory information as customers purchase items.
Advantages of the Perpetual Inventory System
Perpetual inventory systems are common in many modern businesses. They are most often found in large businesses, businesses with multiple locations, or businesses that carry expensive products, such as a jeweler or electronics store. While errors in inventory occur due to loss, breakage, theft, improper inventory tracking, or scanning errors, there are many advantages to using a perpetual inventory system:
- Prevents stock outs; a stock out means that a product is out of stock
- Gives business owners a more accurate understanding of customer preferences
- Allows business owners to centralize the inventory management system for multiple locations
- Provides greater accuracy due to each inventory item being recorded on a separate ledger
- Gives valuable information to business owners, such as discounts, purchases, and returns
- Reduces physical inventory counts
Example of a Perpetual Inventory System
Omar works for ABC Pool Equipment Company. It is his job to manage the inventory. There is an inventory of over 5000 parts. Each part cost from $50 to $500. Omar knows that with such a large, expensive inventory he needs to be able to control inventory and know exactly what he has on hand for each part. He has decided that implementing a perpetual inventory system is the best solution.
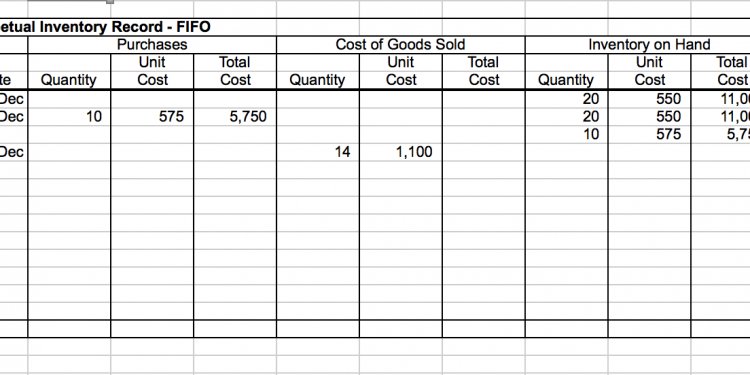
Using barcodes on each inventory item and RFID scanners, workers are able to assist Omar in keeping track of each part that is received, moved, or sold. On March 15, 2014, Omar saw that there were only 49 above ground pool pumps in inventory. He placed an order for 50 more pumps. On April 1, 2014, 50 above ground pool pumps costing $100 each were received and scanned into inventory.
The pumps were placed on row D in section 6 on shelf B in bin 4 or D-6-B-4 with the previous inventory of 49 pumps. Every time a pump is sold, a work order is produced that sends workers to D-6-B-4 to retrieve the part. Workers scan the part and the barcode of the location of the part, enter the number the work order requires, and save the record. The part is then updated in the computer system.
Unlock Content
Over 30, 000 lessons in all major subjectsGet FREE access for 5 days,
just create an account.
No obligation, cancel anytime.
Want to learn more?Select a subject to preview related courses:
Each time anything occurs that affects inventory, the perpetual inventory system updates the ledger for a specific part. For instance, the ledger reflected that on March 15 there were 49 pumps in inventory, totaling $4, 900. On April 1, the ledger was updated to reflect that there were 99 pumps in inventory, totaling $9, 900. Twelve pumps were sold on April 4, 2014, and the ledger reflected that there were 87 pumps in inventory, totaling $8, 700. Another six pumps were sold and one pump returned on April 7, 2014, and the ledger reflected that there were 82 pumps in stock, totaling $8, 200.
Lesson Summary
A perpetual inventory system, or a continuous inventory system, is an inventory control system that allows users to keep a more accurate account of inventory on hand. It became popular after the 1970s when the use of computers became more widespread. Inventory on hand is updated whenever a transaction is made. It works in conjunction with other technology, such as barcodes, radiofrequency identification or RFID, and point of sales or POS.